By Franck Kuwonu
As African economies look to the brand new yr, nations throughout the continent are poised to make reasonable financial good points however should navigate the maze of home and worldwide challenges.
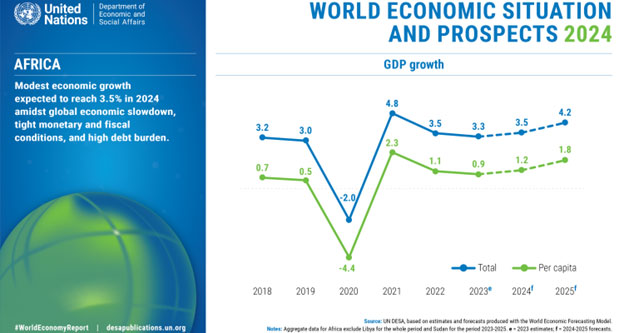
In accordance with the UN World Financial State of affairs and Prospects (WESP) 2024, the continent’s financial development is predicted to quicken barely, with common GDP presumably inching as much as 3.5 per cent.
But, debt sustainability considerations, fiscal pressures, and local weather change current uncertainties. The projected 3.5 per cent development is a slight enhance from the three.3 per cent in 2023.

Main regional economies, akin to that of Egypt, are anticipated to sluggish to three.4 per cent from 4.2 within the earlier yr, primarily attributable to overseas change scarcities which will weaken import capability and home demand.
In South Africa, the persistent vitality disaster has restricted the expansion to only 0.5 per cent in 2023, and no vital change is predicted in 2024.
In Nigeria, the nation’s development prospect factors to a reasonable enhance, largely attributable to authorities reforms within the oil sector. The expansion is forecast to be at 3.1 per cent.
Debt burden
Excessive ranges of debt are one of many primary challenges African economies face going ahead, the report famous. As an example, Zambia is navigating a debt-to-GDP ratio that soared previous 70 per cent lately.
But, the nation shouldn’t be alone: “18 nations in Africa recorded a debt-to-GDP ratio of over 70 per cent in 2023, with lots of them dealing with debt misery,” the UN Division of Financial and Social Affairs (UN DESA) stated in a launch accompanying the report.
Ghana’s monetary well being can be below scrutiny, with a staggering fifth of its tax income dedicated to servicing debt. These cases usually are not anomalies however somewhat stark representations of the debt dilemma many African nations confront.
Fiscal well being and inflation
Fiscal stability stays elusive, the report highlighted, with many nations wrestling to extend their tax income, a significant lifeline for financial sustainability.
Vitality subsidy reforms in nations like Nigeria and Angola replicate makes an attempt to recalibrate fiscal insurance policies amidst urgent financial realities. On the similar time, inflationary pressures are widespread, with nations like Nigeria and Egypt experiencing extreme surges in meals costs.
In response, Central banks throughout the continent have tightened financial insurance policies, making an attempt to stabilize currencies and curb inflation. But, the effectiveness of those measures within the face of world financial turbulence stays a important query.
Local weather change
Local weather change continues to be an unpredictable catalyst, considerably impacting agriculture-dependent economies. The Horn of Africa, repeatedly battered by droughts exacerbated by human-induced local weather change, faces ongoing threats to meals safety and financial stability.
Southern Africa’s vulnerability was laid naked by Cyclone Freddy in March 2023, with losses mounting into tons of of tens of millions. These incidents underscore the pressing want for local weather resilience methods.
Commerce
The worldwide slowdown in commerce has additionally slowed down financial development in Africa. This is because of much less demand from the primary nations that purchase Africa’s exports and the costs for uncooked supplies and items bought by the continent have stopped growing.
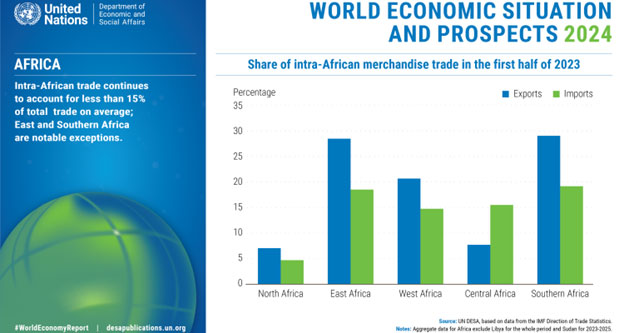
Though total intra-African commerce stays comparatively low continent-wide, hovering under 15 per cent, this normal pattern masks regional variations.
Notably, East and Southern Africa stand out with their comparatively increased ranges of intra-regional commerce, the place intra-African exports correspond to virtually 30% of those subregions’ total exports. These areas distinction with different elements of the continent, the place commerce is extra externally oriented.
The African Continental Free Commerce Space (AfCFTA) emerged as a central initiative supposed to deal with these intra-African commerce points. Its aim is to reinforce financial integration and enhance commerce flows inside the continent by making a single marketplace for items and providers.
But, regardless of its potential, the precise affect of AfCFTA has been restricted thus far, the report stated.
The 2024 UN World Financial State of affairs and Prospects (WESP) is produced by UN DESA in partnership with the 5 UN Regional Commissions, UNCTAD, UN-OHRLLS and UNWTO. It options the worldwide financial outlook for 2024 and 2025, and regional development forecasts for developed and creating economies, in addition to economies in transition.
The total report is obtainable at: https://desapublications.un.org/
Supply: Africa Renewal, United Nations
IPS UN Bureau
